A wetsuit keeps the wearer warm by trapping a thin layer of water between its neoprene fabric and the skin. This water heats up from body heat, providing insulation.
Wetsuits are essential gear for many water sports enthusiasts, offering thermal protection in chilly waters. Made primarily from neoprene, a type of synthetic rubber, wetsuits come in various thicknesses tailored to different water temperatures. The neoprene material not only traps water that is then warmed by the body’s natural heat but also provides buoyancy and protection against UV rays and abrasions.
Proper fit is crucial as it ensures minimal water exchange, maximizing the suit’s effectiveness in insulating against the cold. By offering a blend of flexibility and warmth, wetsuits enable swimmers, surfers, and divers to enjoy their activities for extended periods, regardless of the water temperature.
Understanding Wet Suits
Embarking on an aquatic adventure often necessitates the right gear, and a crucial element of this equipment is the wet suit. This attire is not just a fashion statement but a sophisticated tool designed to enhance and protect the body while immersed in water. Let’s dive into the science and function of wet suits, unraveling how they equip oceanic explorers and enthusiasts to brave the chilling depths of waters around the world.
Purpose Of Wet Suits
Wet suits serve multiple critical purposes, foremost among them being thermal protection. When submerged, the human body loses heat up to 25 times faster compared to air, which necessitates an insulating layer. The wet suit’s primary job is to slow down this heat loss, allowing swimmers, surfers, and divers to stay in cold water for extended periods. Besides insulation, wet suits also offer physical protection from environmental hazards such as UV rays, abrasions, and stings from marine life. Additionally, they can provide buoyancy and flexibility, aiding in better swimming performance.
Insulating Materials
The insulating prowess of wet suits hinges on the materials used in their construction. Primarily made from neoprene, a synthetic rubber full of tiny gas bubbles, they trap water between the suit and the skin. Here is how it works:
- Trapped Water Layer: Once a thin layer of water infiltrates the suit, the body warms it up, forming a warm water barrier.
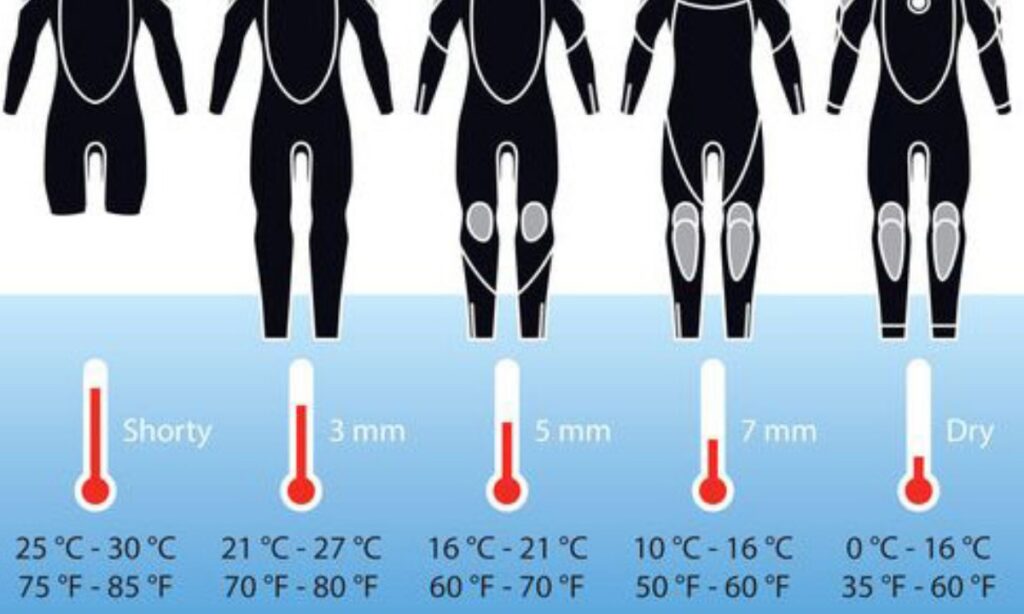
- Thickness: The thickness of the neoprene ranges from 2mm to 8mm, providing different levels of insulation for varying climates and water temperatures.
- Gas Bubbles: The microscopic gas bubbles in the neoprene are key for reducing heat conduction, enhancing the suit’s thermal protection.
Modern seafarers will find wet suits integrated with additional materials like thermal linings or titanium weaves to further augment warmth and comfort. The technique of seam construction—blind stitching, flat-lock, or taped—can also impact the insulating efficiency of the suit.
Neoprene Technology
Dive into the remarkable world of Neoprene Technology—the material that has revolutionized water sports and safety gear. This synthetic rubber isn’t just durable; it’s a thermal-insulating powerhouse, providing surfers, divers, and swimmers with the warmth they need in the chill of the ocean.
Understanding how wetsuits keep you warm begins with a closer look at their key ingredient: neoprene. This material is engineered to retain heat and resist water, making it ideal for prolonged immersion in aquatic environments.
Properties Of Neoprene
Neoprene comes with an array of impressive features:
- Flexibility: Adapts to body movements without losing shape.
- Durability: Resistant to degradation from sun, oil, and chemicals.
- Buoyancy: Provides lift, aiding swimmers and divers to float.
- Water Resistance: Its closed-cell structure minimizes water absorption.
Thermal Insulation
At the heart of neoprene’s success is its thermal insulation property. It works based on a simple yet effective principle:
- Neoprene traps a thin layer of water between the suit and the skin.
- The body naturally warms this water up.
- The insulating foam prevents this heat from escaping.
The result is a warm, protective layer that keeps body temperatures from plummeting in cold waters. The thickness of the neoprene greatly influences the level of insulation. Thicker suits offer more warmth but can impede movement, so there’s a balance to strike based on the water conditions and activity.
Mechanism Of Heat Retention
Functionality meets science in the fascinating design of a wetsuit. Essential for many water-based activities, a wetsuit’s core purpose is to retain body heat in cold water environments. Understanding how this is achieved involves exploring the thickness of the material, along with the interaction between water and body heat.
Thickness And Warmth
The thickness of the wetsuit is pivotal to its thermal retention capabilities. Wetsuits come in varied thicknesses measured in millimeters, often indicated with two numbers separated by a slash. The first number represents the thickness around the core, while the second is for the limbs.
- 3/2mm: Suitable for moderate water temperatures.
- 5/4mm: Ideal for colder conditions, offering enhanced insulation.
A thicker wetsuit provides greater insulation due to a simple principle: thicker material increases the amount of water that can be trapped and warmed up by the body heat, forming a thermal barrier. However, it’s vital to balance warmth with flexibility.
Water And Body Heat Interaction
Despite being submerged in cold water, the human body continuously generates heat. A wetsuit capitalizes on this by trapping a thin layer of water right against the skin. It’s not the water itself, though, that maintains your warmth but rather the heat your body imparts to this confined layer.
- Water enters the wetsuit through various openings.
- Body heat warms up this trapped water layer.
- The neoprene material insulates this warm layer, preventing it from escaping.
Neoprene, containing thousands of tiny gas bubbles, provides excellent thermal insulation. This is because gases are poor conductors of heat, making the suit’s material inherently resistant to heat flow, thus preserving body temperature in challenging conditions.
Proper Fit And Function
Embarking on an aquatic adventure with a wetsuit requires more than just selecting any snug body cover. The proper fit and function of a wetsuit are paramount; they are your second skin in the deep blue, a critical factor in warmth, comfort, and mobility. This skin doesn’t just keep you warm—it also grants you the freedom to glide and maneuver through the water effortlessly. Below, we dive into the critical aspects of wetsuit functionality, exploring how to achieve the ideal balance between body coverage and flexibility.
Body Coverage
Body Coverage
The extent of your wetsuit’s body coverage is integral to its overall effectiveness. It’s not only about preventing hypothermia but also about reducing drag and protecting against sunburns and scrapes. Wetsuits come in varying styles, from full suits to spring suits, each designed for different conditions and activities. Full suits cover the entire body, sans hands, feet, and face, while spring suits might leave lower arms and legs exposed, offering a cooler option for mild climates.
- Full Suits: Extensive coverage ideal for cold water.
- Spring Suits: Less coverage suitable for warmer water.
- Rash Guards: Minimal coverage for UV protection and rash prevention.
Achieving the right balance in coverage is vital; too much can overheat the body in warm waters, and too little can lead to rapid heat loss in colder conditions.
Flexibility and Movement
Flexibility And Movement
A quality wetsuit must offer optimal flexibility and movement. The wetsuit’s material and construction should allow for the full range of motion, making activities like paddling, swimming, and diving feel natural. Neoprene, a stretchable synthetic rubber, is the primary fabric providing both insulation and flexibility.
Flexibility does not come at the expense of a snug fit. The wetsuit needs to contour closely to the body, ensuring minimal water enters. However, it shouldn’t be so tight that it restricts movement or blood circulation. Check the fit around high-mobility areas:
| Area | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Armpits and Groin | No bunching of material, must allow free arm and leg movement. |
| Shoulders | Enough stretch for full arm rotation without resistance. |
| Knees and Elbows | Pre-formed material for ease of bending without restriction. |
When trying on wetsuits, simulate the motions of your water sport to ensure the suit’s stretch does not hinder performance.
FAQ
Does Your Body Stay Dry Under A Wetsuit?
Your body doesn’t stay completely dry under a wetsuit. A thin layer of water gets trapped between the suit and your skin, aiding in insulation.
Do Your Clothes Get Wet Under A Wetsuit?
Yes, a small amount of water enters your wetsuit and warms up to body temperature, which helps maintain warmth. Your clothes underneath may get damp.
How Does Water Get Inside A Wetsuit?
Water enters a wetsuit through seams, zippers, neck, wrist, and ankle openings. This trapped water then warms to body temperature, creating insulation.
Do You Wet A Wetsuit Before Putting It On?
Wetting a wetsuit before putting it on is not necessary, but some people find it easier to slide on when damp. It can also help with temperature regulation if using cold water.
Conclusion
Diving into the deep, a wetsuit is an essential ally. It cleverly traps a thin water layer, using body warmth for insulation. This gear enables extended aquatic adventures, even in cooler temperatures. Remember, the right fit ensures maximum effectiveness. So gear up, stay warm, and embrace the wonders beneath the waves.
